Key Stage 3 maths worksheets – Resources for whole curriculum

An entire breakdown of the KS3 maths curriculum in England with worksheets, activities, ideas, PowerPoints and more for every element…

- by Teachwire
- Classroom expertise and free resources for teachers

Unlock a treasure trove of free Key Stage 3 maths worksheets tailored to the curriculum. These worksheets will save you time and boost students’ learning.
We’ve split this post up into six main areas. Underneath each area we’ve outlined the Key Stage 3 maths curriculum and highlighted worksheets and lesson plans that you can download right here on Teachwire – for free!
Key Stage 3 maths worksheets
Free homework question packs
Help students practise their maths skills at home with these free Key Stage 3 maths worksheets for Year 7, Year 8 and Year 9.
100+ problem-solving questions

You can also download 100+ problem-solving questions in our KS3 maths worksheets pack from White Rose Maths.
Mega KS3 revision PowerPoint
We also have a mega KS3 maths questions PowerPoint featuring 100+ slides of questions on a range of topics, with answers included.
KS3 maths quiz
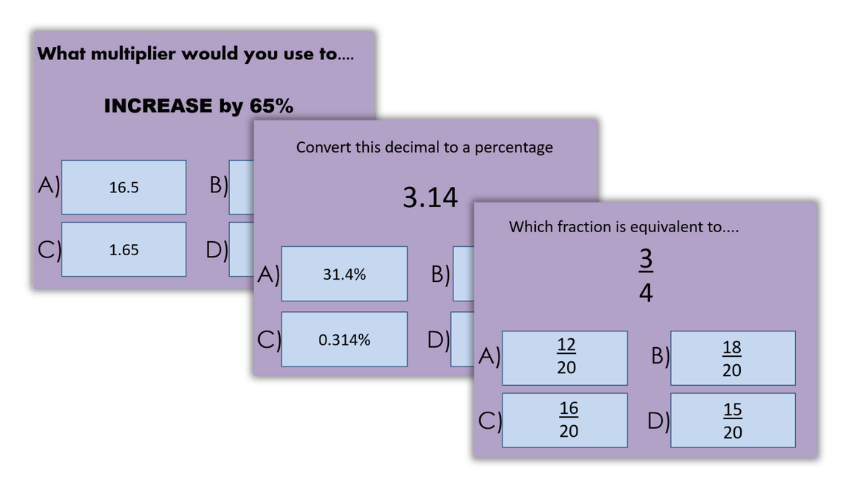
This comprehensive maths quiz PowerPoint offers 30 multiple-choice quizzes spread across over 300 slides. It’s perfect for KS3 and GCSE students and covers a wide array of topics.
Number
Place value
- Understand and use place value for decimals, measures and integers of any size
Resource: Use this set of problem cards to get children thinking about place value with decimals.
Ordering and number lines
- Order positive and negative integers, decimals and fractions
- Use the number line as a model for ordering of the real numbers
- Use the symbols =, ≠, <, >, ≤, ≥
Resource: This Key Stage 3 maths worksheet covers negative numbers. Pupils will add positive values to negative values.
Or try this ordering fractions and decimals worksheet. It contains questions which require students to think about the relative sizes of fractions and decimals, and the order that they would be written on a number line.
Four operations
- Use the four operations, including formal written methods, applied to integers, decimals, proper and improper fractions, and mixed numbers, all both positive and negative
Resources: This adding fractions with the same denominator worksheet gives pupils the opportunity to practice fluency, reasoning and problem-solving.
This adding and subtracting fractions worksheet lets students pick the section on which they need more work.
These maths codebreakers cover a wide range of maths topics including multiplying and dividing fractions.
This simple PowerPoint for multiplying and dividing fractions shows how simplifying can be done before the multiplying.
Priority of operations and relationships between them
- Use conventional notation for the priority of operations, including brackets, powers, roots and reciprocals
- Recognise and use relationships between operations including inverse operations
Resources: This order of operations worksheet encourages pupils to recognise that we need to reduce calculations to those involving sums and difference.
These four carefully thought-out worksheets will help your class take their first steps working with the order of operations.
Meanwhile, these PowerPoints cover the precedence of operations, making it clear that multiplication/division have the same precedence as each other, as do addition/subtraction.
Integer powers and real roots
- Use integer powers and associated real roots (square, cube and higher)
- Recognise powers of 2, 3, 4, 5
- Distinguish between exact representations of roots and their decimal approximations
Resource: This three-part lesson covers finding squares, cubes and square roots. There are also mini-plenary and plenary activities, with answers.
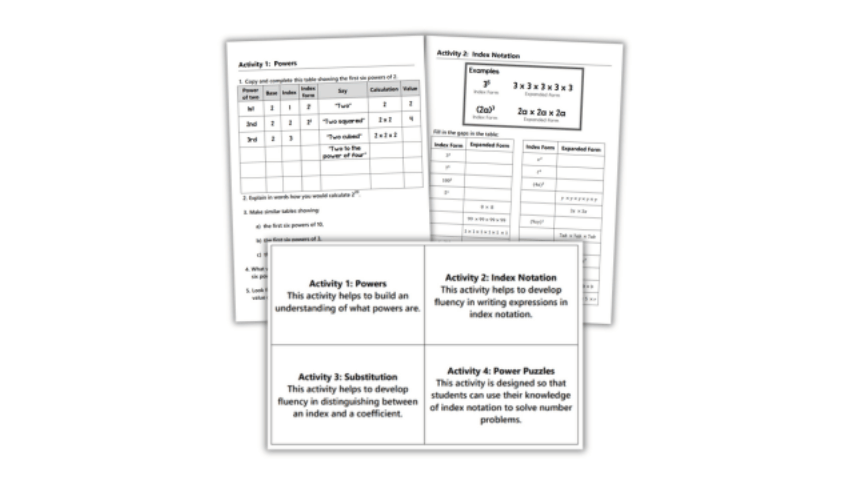
This activity helps to build an understanding of what powers are. Students need to copy and complete the table showing the first six powers of 2. They then need to explain in words how they would calculate 220, before making similar tables showing the first six powers of 10, 3 and a.
Comparing numbers
- Interpret and compare numbers in standard form A x 10n 1≤A<10, where n is a positive or negative integer or zero
Resources: This worksheet and PowerPoint explain why putting numbers in standard form is useful and how to use the x10^ button on your calculator
These maths codebreakers cover standard from, among other topics. Unjumble the letters to find out the answer to some (very bad) jokes.
Terminating decimals
- Work interchangeably with terminating decimals and their corresponding fractions (such as 3.5 and 7/2 or 0.375 and 3/8)
Resource: Use this resource to think about the relative sizes of fractions and decimals, and the order that they would be written on a number line.
At the end of these fractions, decimals and percents worksheets students will look at fractions that produce terminating decimals.
Percentages
- Define percentage as ‘number of parts per hundred’
- Interpret percentages and one quantity as a percentage of another
- Compare two quantities using percentages
- Work with percentages greater than 100%

Resource: This percentage calculations worksheet includes different types of percentage questions with answers.
Alternatively, use this PowerPoint and worksheets to introduce students to the method of calculating percentages without a calculator.
Operators
- Interpret fractions and percentages as operators
Resources: This fractions, decimals and percents worksheet includes recurring decimals and values greater than 1.
Meanwhile, this resource covers simplifying, converting recurring decimals to fractions and everything in between.
Units of measurement
- Use standard units of mass, length, time, money and other measures, including with decimal quantities
Resource: This units of measurement worksheet covers simple conversions, metric to imperial and area conversion.
Rounding up
- Round numbers and measures to an appropriate degree of accuracy [for example, to a number of decimal places or significant figures]
Resource: Use this rounding and approximation worksheet to practise rounding a number to a given number of decimal places or significant figures.
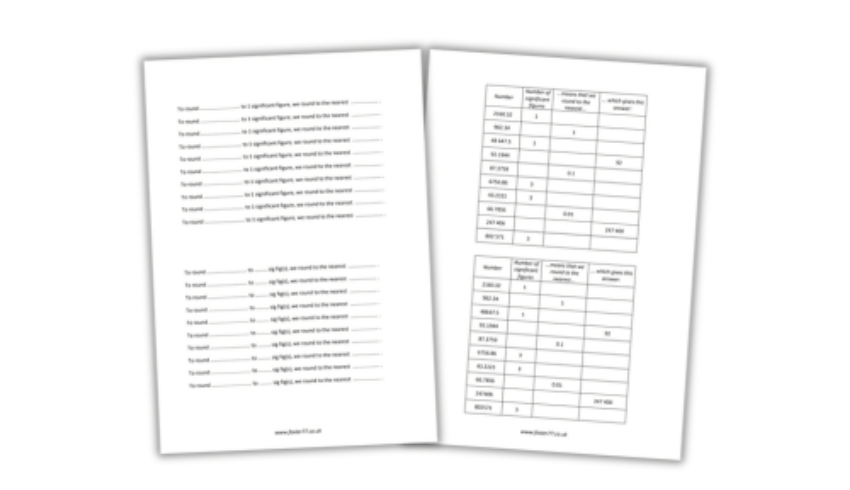
This free rounding numbers worksheet helps students avoid getting in a muddle with zeroes and columns when rounding numbers.
Approximation
- Use approximation through rounding to estimate answers and calculate possible resulting errors expressed using inequality notation a<x≤b
Resource: This resource takes you from basic rounding to whole numbers up through decimal places, significant figures and beyond.
Calculating
- Use a calculator and other technologies to calculate results accurately and then interpret them appropriately
Resources: This lesson plan runs through calculator basics and there’s a tarsia puzle and past papers to practise on.
This PowerPoint presentation explains every single button and mode on standard black Casio calculators.
Algebra
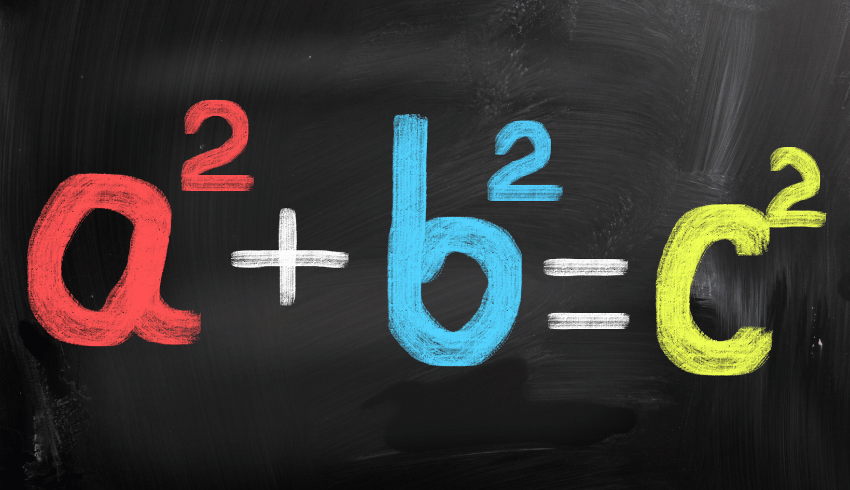
Algebraic notation
Use and interpret algebraic notation, including:
- ab in place of a × b
- 3y in place of y + y + y and 3 × y
- a2 in place of a × a
- a3 in place of a × a × a
- a2b in place of a × a × b
- a/b in place of a ÷ b
- coefficients written as fractions rather than as decimals
- brackets
Resource: This KS3 maths formula sheet first asks students to link each statement with a formula in the given table. They then move on to writing their own formula for each of the given statements.
This resource covers algebraic notation and simplifying by collecting like terms and multiplying/dividing expressions, as well as substituting values.
Substituting
- Substitute numerical values into formulae and expressions, including scientific formulae
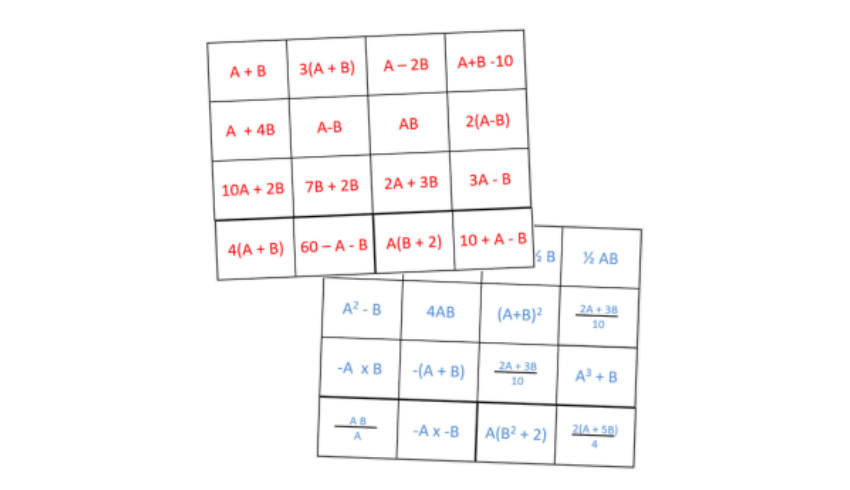
Resource: This resource on the topic of algebra substitution gets pupils working in pairs and practising substituting values into expressions.
This algebra resource tasks students with playing a Connect 4-style game of connecting four squares to learn about how to substitute in simple and more complex algebraic expressions.
This nine-lesson simplifying expressions PowerPoint takes students from the most basic simplifying up through substitution and proof of formulae.
Expressions, equations, inequalities, terms and factors
- Understand and use the concepts and vocabulary of expressions, equations, inequalities, terms and factors
Resource: This algebraic expressions resource covers algebraic notation and simplifying, substituting values and forming algebraic expressions.
Maintaining equivalence
Simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions to maintain equivalence by:
- collecting like terms
- multiplying a single term over a bracket
- taking out common factors
- expanding products of two or more binomials
Resources: These Key Stage 3 maths worksheets feature funny codebreakers covering a wide range of maths topics, including simplifying expressions.
This algebraic expressions resource covers algebraic notation and simplifying, substituting values and forming algebraic expressions.
Formulae
- Understand and use standard mathematical formulae
- Rearrange formulae to change the subject
Resources: This worksheet contains the full range of exam-type questions that require students to simplify algebraic fractions by factorising.
This free algebraic fractions worksheet with answers asks students to factorise then simplify algebraic fractions.
Modelling and graphs
- Model situations or procedures by translating them into algebraic expressions or formulae and by using graphs
Resource: This full lesson introduces solving simultaneous equations using graphical methods.
Linear equations
- Use algebraic methods to solve linear equations in one variable (including all forms that require rearrangement)
Resources: Use these matching activities to join equations that match the central cloud but also solve the ones that don’t match.

These four solving equations worksheets from Cazoom Maths range from levels 4-7.
This algebra worksheet contains four pages of questions on solving linear equations of increasing complexity.
Coordinates
- Work with coordinates in all four quadrants
Resource: This 4 quadrants coordinates worksheet will get your KS3 students practising plotting and identifying coordinates in all four quadrants.
Graphs
Recognise, sketch and produce graphs of linear and quadratic functions of one variable with appropriate scaling, using equations in x and y and the Cartesian plane
Resource: This worksheet covers sketching quadratic graphs by finding out where the graph crosses each axis.
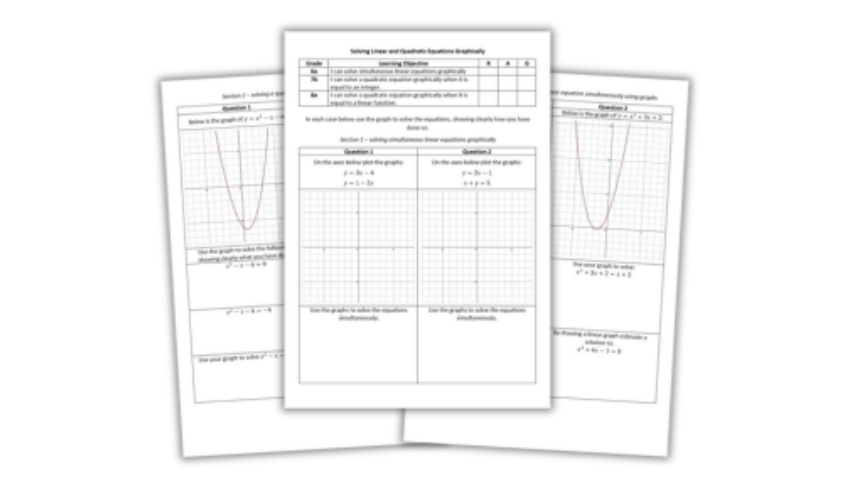
This worksheet about solving simultaneous equations graphically features questions on solving a quadratic that is equal to an integer and solving a quadratic and linear equation simultaneously using graphs.
Interpreting relationships
- Interpret mathematical relationships both algebraically and graphically
Resource: This solving simultaneous equations graphically worksheet covers solving a quadratic that is equal to an integer and solving a quadratic and linear equation simultaneously using graphs.
Reducing and interpreting
- Reduce a given linear equation in two variables to the standard form y = mx + c
- Calculate and interpret gradients and intercepts of graphs of such linear equations numerically, graphically and algebraically
Resource: This lesson introduces the general form of all straight line graphs (y=mx+c), explaining the key features.
Linear and quadratic graphs
- Use linear and quadratic graphs to estimate values of y for given values of x and vice versa
- Find approximate solutions of simultaneous linear equations
Resource: This lesson will show students how plotting two linear equations in x and y allows them to solve simultaneous equations.
Graphs of a variety of functions
- Find approximate solutions to contextual problems from given graphs of a variety of functions, including piece-wise linear, exponential and reciprocal graphs
Resource: Cut the right coloured wires to save everyone in this ‘Defuse the bomb’ worksheet. This involves basic and more complicated linear graphs, quadratics and non-linear graphs (cubics, reciprocals and exponentials).
Terms of a sequence
- Generate terms of a sequence from either a term-to-term or a position-to-term rule
Resources: Use this resource to draw the next pattern and find the nth term of an arithmetic sequence.
This resource features a discussion of what sequences are and builds to the term-to-term rule.
Arithmetic sequences
- Recognise arithmetic sequences and find the nth term
Resources: These nth term worksheets contain material that is typically introduced at KS3.

This arithmetic sequence worksheet helps students master arithmetic sequences through an array of thoughtfully curated questions.
Geometric sequences
- Recognise geometric sequences and appreciate other sequences that arise
Resource: This resource covers a recap of linear sequences, geometric sequences, quadratic sequences and sequence proofs.
Ratio, proportion and rates of change
Standard units
- Change freely between related standard units [for example time, length, area, volume/capacity, mass]
Resource: This ratio and proportion resource includes methods for solving problems involving direct and indirect proportion and problems involving ratio.
Scale factors, scale diagrams and maps
- Use scale factors, scale diagrams and maps
Resources: This Key Stage 3 maths worksheet covers enlargement with negative scale factors. It involves enlarging shapes to produce a picture. There’s also this scale factors worksheet.
Expressing quantities as a fraction of another
- Express one quantity as a fraction of another, where the fraction is less than 1 and greater than 1
Resource: This worksheet involves finding fractions of amounts. The extension is an equivalent fraction investigation.
Ratio notation
- Use ratio notation, including reduction to simplest form
Resource: In this simplifying ratios worksheet, students need to fully simplify a ratio and write it as a unitary ratio.
Division
- Divide a given quantity into two parts in a given part:part or part:whole ratio
- Express the division of a quantity into two parts as a ratio
Resources: Use this ratio worksheet to simplify ratios and share amounts by a given ratio.
Alternatively, this simplifying ratios treasure hunt gives students practice at converting ratios into their simplest form by dividing both parts.
Multiplicative relationships
- Understand that a multiplicative relationship between two quantities can be expressed as a ratio or a fraction
Resource: This resource features three lessons on ratio problems, but with an emphasis on using fractions in calculations and not relying on calculators or decimals.
Arithmetic of fractions
- Relate the language of ratios and the associated calculations to the arithmetic of fractions and to linear functions
Resource: These fraction, ratio and percentage reasoning tasks are based on an Edexcel GCSE question about fractions, ratio and percentages of an amount.
Percentage change
Solve problems involving percentage change, including:
- percentage increase, decrease and original value problems
- simple interest in financial mathematics
Resources: This activity involves working out percentage changes in footballers’ wages.
Alternatively, use this Homes Under the Hammer worksheet to calculate whether people have made a profit or loss. There’s also a Storage Hunters version!
In this percentage change KS3 lesson, students explore what happens to a certain amount of money when it undergoes a particular percentage increase or decrease.
Direct and inverse proportion
- Solve problems involving direct and inverse proportion, including graphical and algebraic representations
Resource: This ratio and proportion resource includes methods for solving problems involving direct and indirect proportion.
Compound units
- Use compound units such as speed, unit pricing and density to solve problems
Resource: Use this resource to solve simple problems involving speed, distance, time, density, mass and volume.
Geometry and measures
Perimeter and area
Derive and apply formulae to calculate and solve problems involving:
- perimeter and area of triangles
- parallelograms
- trapezia
- volume of cuboids (including cubes)
- other prisms (including cylinders)
Resources: These maths codebreakers cover a wide range of maths topics including area and perimeter.
Or try this resource where students find the perimeter, circumference and area of a variety of shapes.
Perimeters and areas of 2D shapes
Calculate and solve problems involving:
- perimeters of 2D shapes (including circles)
- areas of circles
- composite shapes
Resource: These two Key Stage 3 maths worksheets cover the area of a circle. They focus on finding areas of circles and circular shapes.
Line segments and angles
- Draw and measure line segments and angles in geometric figures, including interpreting scale drawings
Resource: This simple sheet allows students to practise compass constructions.
Ruler and compass constructions
- Derive and use the standard ruler and compass constructions (perpendicular bisector of a line segment, constructing a perpendicular to a given line from/at a given point, bisecting a given angle)
- Recognise and use the perpendicular distance from a point to a line as the shortest distance to the line
Resource: Construct tool shapes and cut shapes in half using only a ruler and a protractor in this Walking Dead themed worksheet.
Describing, sketching and drawing
Describe, sketch and draw using conventional terms and notations:
- points, lines, parallel lines, perpendicular lines and right angles
- regular polygons and other polygons that are reflectively and rotationally symmetric
Resource: In this reflective symmetry worksheet themed around logos, students will explore the fundamental principles of symmetry through a practical exercise.
Labelling triangles
- Use the standard conventions for labelling the sides and angles of triangle ABC
- Know and use the criteria for congruence of triangles
Resource: This properties of 2D shapes KS3 worksheet asks students to link the shape to the properties. Students need to read each description carefully then draw a line to match up the correct shapes and properties.
Meanwhile, this right-angled triangles matching activity focuses on finding sides and angles.
Properties of shapes
- Derive and illustrate properties of triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and other plane figures using appropriate language and technologies
Resources: Use this PowerPoint listing the properties of quadrilaterals – including angles, equal/parallel sides, line and rotational symmetry and diagonals – as part of your teaching on geometry and measures.
Translations, rotations and reflections
- Identify properties of, and describe the results of, translations, rotations and reflections applied to given figures
Resource: With this resource students will describe and carry out translations, reflections and rotations and identify a single transformation that has the same effect as certain combinations of multiple other transformations.
Constructing shapes
- Identify and construct congruent triangles, and construct similar shapes by enlargement, with and without coordinate grids
Resource: Construct tool shapes and cut shapes in half using only a ruler and a protractor in this Walking Dead themed worksheet.
Properties of angles
- Apply the properties of angles at a point, angles at a point on a straight line, vertically opposite angles
Resource: This KS3 maths worksheet looks at angles on a straight line. The objective is to be able to find missing angles on a straight line and around a point without using a protractor.
Parallel lines
- Understand and use the relationship between parallel lines and alternate and corresponding angles
Resources: Rather than finding particular unknown angles in each parallel lines question, this angles in parallel lines worksheet involves working out any angles possible and justifying your reasoning.
Alternatively, in this activity, students have to solve angle problems and specify each angle fact that they used in a grid.
Finally, this PowerPoint on angles of parallel lines shows alternate, corresponding and interior angles, followed by some questions to practise.
Angle sums
- Derive and use the sum of angles in a triangle and use it to deduce the angle sum in any polygon, and to derive properties of regular polygons
Resource: This activity is perfect for lower secondary students. It allows them to practise calculating angles in isosceles and scalene triangles.
Angles and sides
- Apply angle facts, triangle congruence, similarity and properties of quadrilaterals to derive results about angles and sides, including Pythagoras’ Theorem
- Use known results to obtain simple proofs
Resources: Prevent confusion among your students when studying the intricacies of Pythagoras’ theorem with the aid of this worksheet.
Or try this Pythagoras PRET homework worksheet. In PRET homeworks, pupils practise, recall, extend and think.
Alternatively, this lesson uses Pythagoras’ Theorem to find the distance between coordinates and includes extended and reversed questions.
Right-angled triangles
- Use Pythagoras’ Theorem and trigonometric ratios in similar triangles to solve problems involving right-angled triangles

Resources: This trigonometry lesson introduces sin, cos and tan, with a little quiz and questions at the the end.
Alternatively, this trigonometry resource includes a levelled activity with progressively harder questions.
Finally, this right-angled triangles activity takes students through six matching activities, three on finding sides and three on finding angles.
Solving problems in 3D
- Use the properties of faces, surfaces, edges and vertices of cubes, cuboids, prisms, cylinders, pyramids, cones and spheres to solve problems in 3D
Resource: This advanced trigonometry resource covers 3D Trigonometry, 3D Pythagoras, angles between a line and a plane, angles between two planes and sine/cosine rules.
Mathematical relationships
- Interpret mathematical relationships both algebraically and geometrically.
Resource: This KS3 maths worksheets booklet from White Rose Maths contains over 100 problem-solving questions.
Probability

Probability experiments
- Record, describe and analyse the frequency of outcomes of simple probability experiments involving randomness, fairness, equally and unequally likely outcomes, using appropriate language and the 0-1 probability scale
Resources: This PowerPoint introduces probability and using the probability scale. It then moves on to show how to calculate simple probability using a tube of Smarties.

Alternatively, use these probability worksheets and PowerPoint to cover describing probability, the probability scale, how we calculate probability and more.
In this probability KS3 lesson plan with worksheet, students will carry out an experiment to estimate the probability that when they throw three ordinary dice, they will show consecutive numbers.
Probabilities of all possible outcomes
- Understand that the probabilities of all possible outcomes sum to 1
Resource: This KS3 probability resource contains a coin probability activity, dice probability demo, PowerPoint, worksheet pack and quiz.
Sets
- Enumerate sets and unions/intersections of sets systematically, using tables, grids and Venn diagrams
Resource: Try this probability lesson from Dr Frost Maths.
Theoretical probabilities
- Generate theoretical sample spaces for single and combined events with equally likely, mutually exclusive outcomes
- Use these to calculate theoretical probabilities
Resources: Use this Year 8 resource to help pupils identify the sample space for both a single event and two combined events (eg adding two dice) and use this to calculate probabilities.
Or try this sample spaces and calculating probabilities worksheet to show how a sample space can help when finding combinations of events.
Statistics
Distributions of a single variable
Describe, interpret and compare observed distributions of a single variable through:
- appropriate graphical representation involving discrete, continuous and grouped data
- appropriate measures of central tendency (mean, mode, median) and spread (range, consideration of outliers)
Resources: This worksheet involves finding the median and mean from sets of data, plus calculating the mean from a frequency table and estimating the mean from grouped data.
These funny maths codebreakers cover a wide range of maths topics including average and range.
Tables, charts and diagrams
- Construct and interpret appropriate tables, charts, and diagrams, including frequency tables, bar charts, pie charts, and pictograms for categorical data, and vertical line (or bar) charts for ungrouped and grouped numerical data
Resources: This worksheet covers interpreting statistical graphs. Alternatively, these tutorials cover everything from bar charts to histograms and simple averages to estimating their mean.
In this lesson, students learn how to calculate the angles of the sectors in a pie chart for various data presented in frequency tables.
Scatter graphs
Describe simple mathematical relationships between two variables (bivariate data) in observational and experimental contexts and illustrate using scatter graphs.
Resources: In this lesson students draw and interpret scatter diagrams, identify correlation, draw a line of best fit and more.
Or try this PowerPoint and worksheet on plotting scatter graphs, identifying correlation and using lines of best fit.
Finally, help out the famous Weatherfield residents of Coronation Street with their data issues by drawing and using scatter graphs.
Browse more KS3 maths games and lesson ideas and GCSE maths games.